Can Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency be Cured?
No
No cure; management focuses on symptom relief and supportive care; lung or liver transplant may be considered in severe cases
What is Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency?
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency is a genetic disorder that can lead to lung and liver disease. It occurs when the body does not produce enough of a protein called alpha-1 antitrypsin. Treatment may involve medications and, in some cases, lung or liver transplantation.
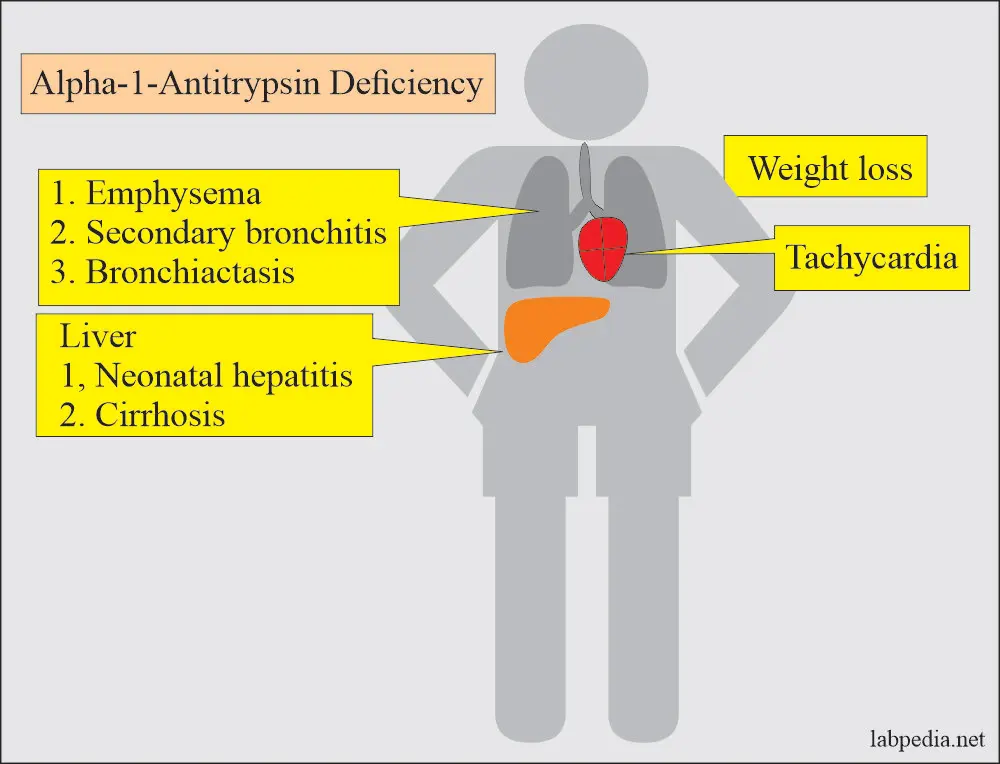
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Genetic disorder leading to a deficiency of alpha-1 antitrypsin, affecting the lungs and liver

Symptoms
Lung problems (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease – COPD), liver disease

Diagnosis
Genetic testing, lung function tests

Prognosis
Variable; depends on the severity of the condition

Complications
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, liver disease
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Genetic mutations affecting the SERPINA1 gene

Treatments
Supportive care, management of symptoms, sometimes lung/liver transplant

Prevention
Supportive care, management of symptoms, sometimes lung/liver transplant
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Autosomal recessive genetic disorder; can lead to lung and liver problems

Patient Perspectives
Lifestyle modifications and supportive care are important for management
For personalized advice and care, always seek the assistance of healthcare professionals. This information is meant for general understanding and not as a replacement for professional medical advice.
Share: