Can Acute Myeloid Leukemia be Cured?
Maybe
Response to treatment varies, some achieve remission, while others may relapse
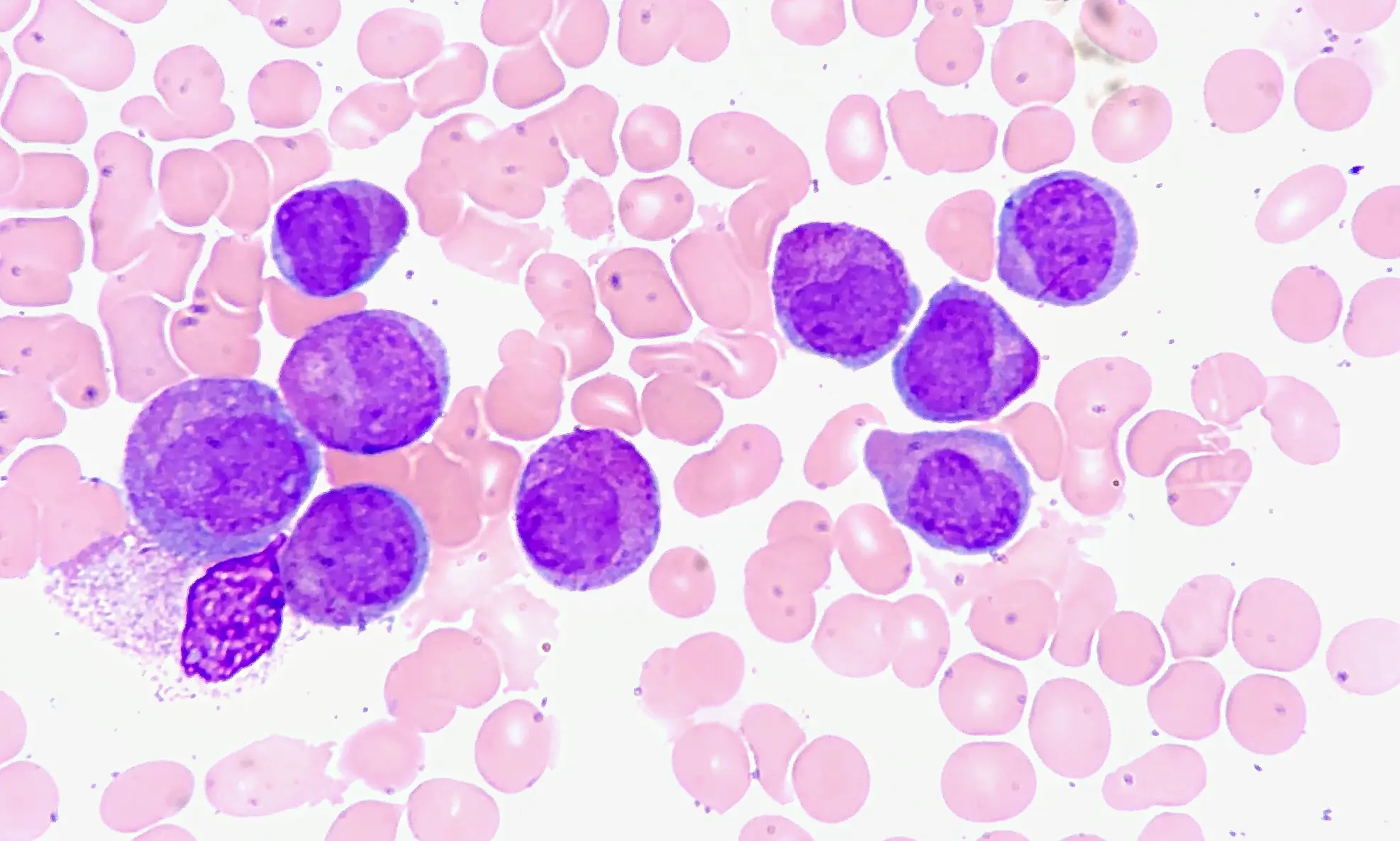
What is Acute Myeloid Leukemia?
Acute myeloid leukemia is a type of blood cancer affecting myeloid cells. Treatment involves chemotherapy and, in some cases, stem cell transplantation. Regular monitoring is essential for assessing the response to treatment and managing potential complications.
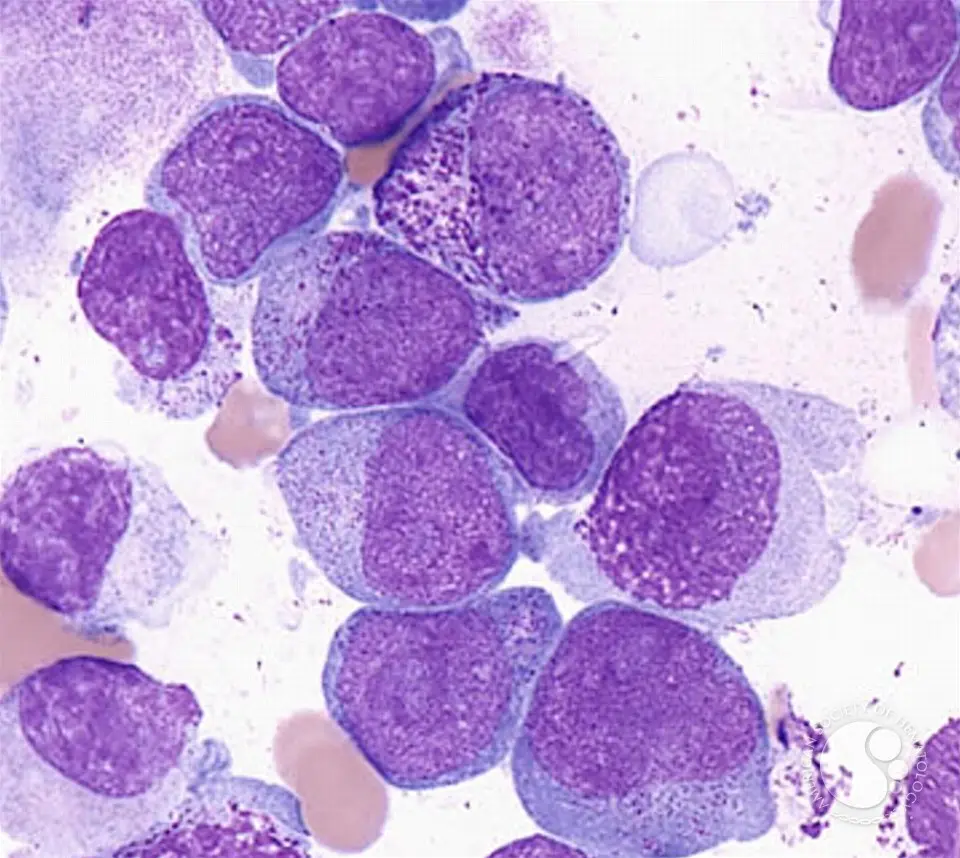
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Rapid growth of abnormal white blood cells

Symptoms
Fatigue, easy bruising, frequent infections

Diagnosis
Blood tests, bone marrow biopsy

Prognosis
Variable; prognosis depends on various factors

Complications
Infection, bleeding, relapse
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Genetic mutations, exposure to certain chemicals

Treatments
Chemotherapy, stem cell transplant

Prevention
Chemotherapy, stem cell transplant
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Increases with age, more common in adults

Patient Perspectives
Intensive chemotherapy and stem cell transplantation may be necessary
Please remember that this information is provided for general understanding, and individual cases may vary. Always consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and information.
Share: