Can Hereditary Angioedema be Cured?
No
No cure; management involves preventing and treating swelling episodes; medications can be effective in controlling symptoms, allowing individuals with hereditary angioedema to lead normal lives
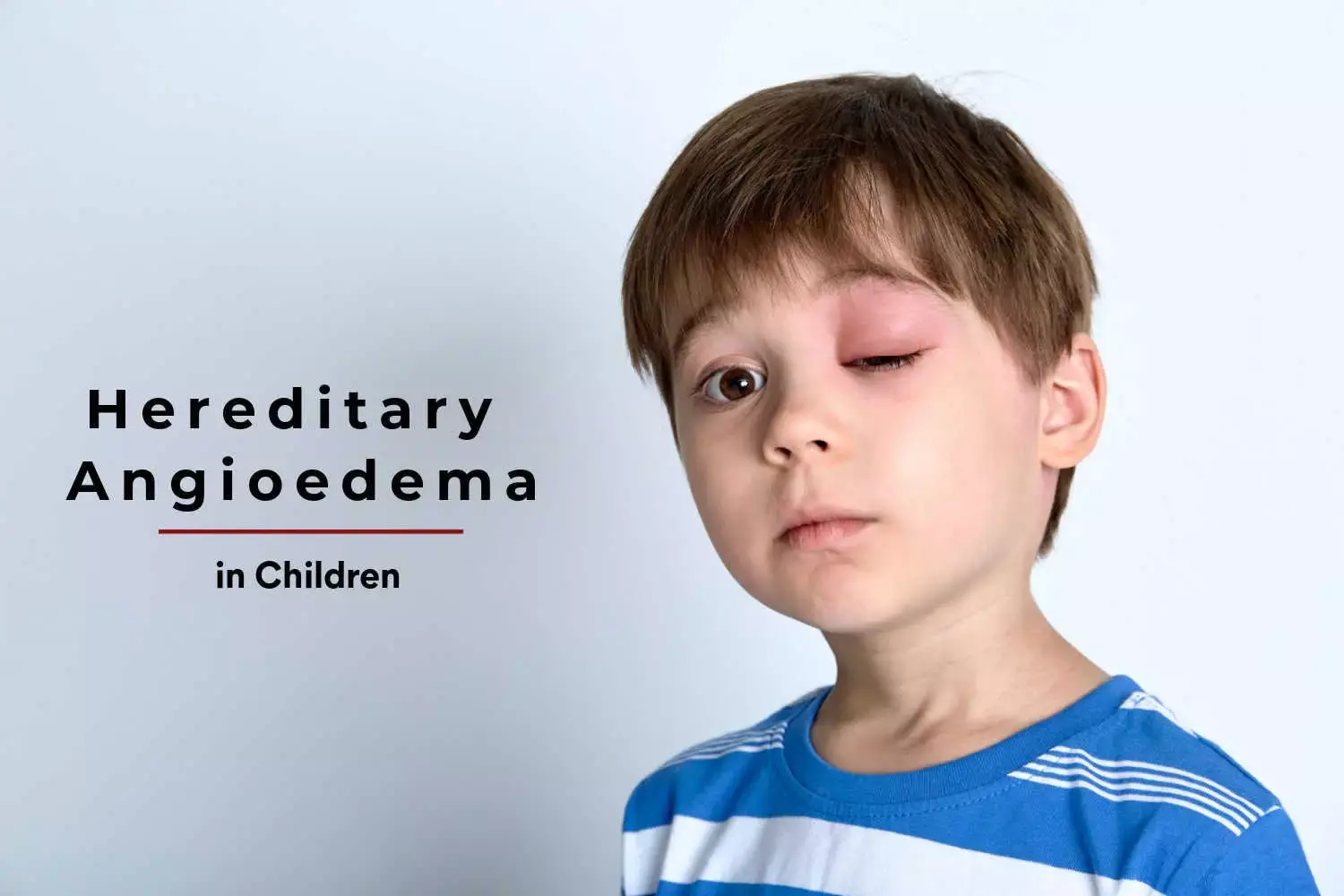
What is Hereditary Angioedema?
Hereditary angioedema is a genetic disorder characterized by episodes of severe swelling, often affecting the face and throat. It is caused by a deficiency or dysfunction of a certain protein. Management includes medications to prevent and treat episodes and support during acute attacks.
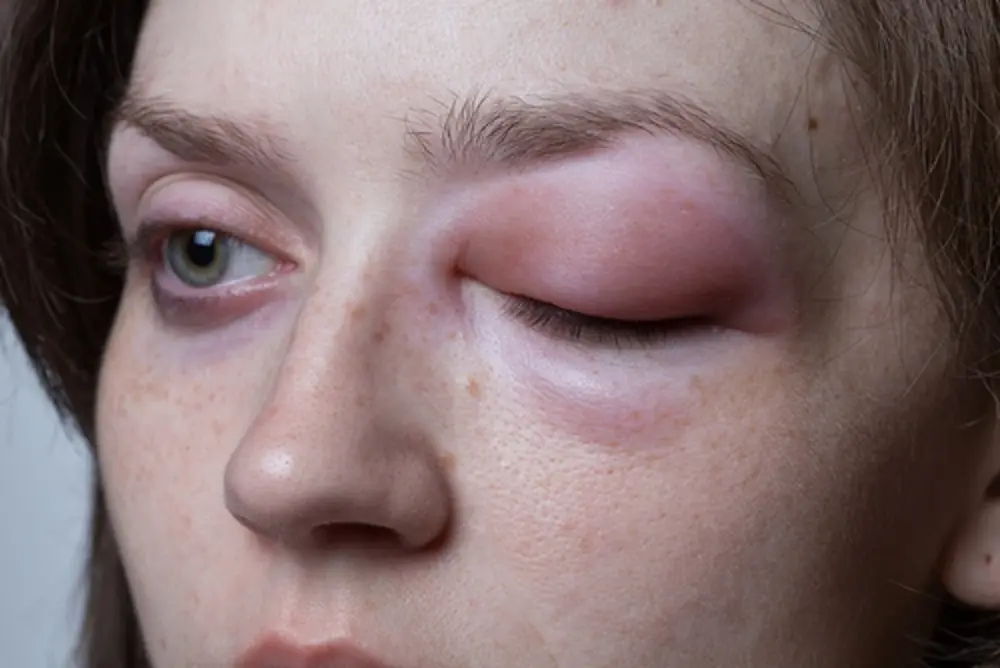
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Genetic disorder causing episodes of severe swelling, often in the face, throat, and abdomen

Symptoms
Recurrent episodes of swelling (angioedema), abdominal pain, difficulty breathing

Diagnosis
Clinical evaluation, sometimes blood tests

Prognosis
Generally good with appropriate management

Complications
Swelling episodes, complications affecting daily life
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Genetic mutations affecting the C1 inhibitor gene, leading to uncontrolled activation of certain proteins in the body

Treatments
Medications (C1 inhibitor replacement, bradykinin receptor antagonists), management of triggers and symptoms

Prevention
Medications (C1 inhibitor replacement, bradykinin receptor antagonists), management of triggers and symptoms
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Genetic disorder causing recurrent episodes of swelling

Patient Perspectives
Medications, supportive care
As always, consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and care.
Share: