Can Familial Adenomatous Polyposis be Cured?
No
No cure; management involves surveillance and intervention to prevent the development of colorectal cancer; individuals with the condition often undergo regular screenings and may opt for surgery to reduce cancer risk
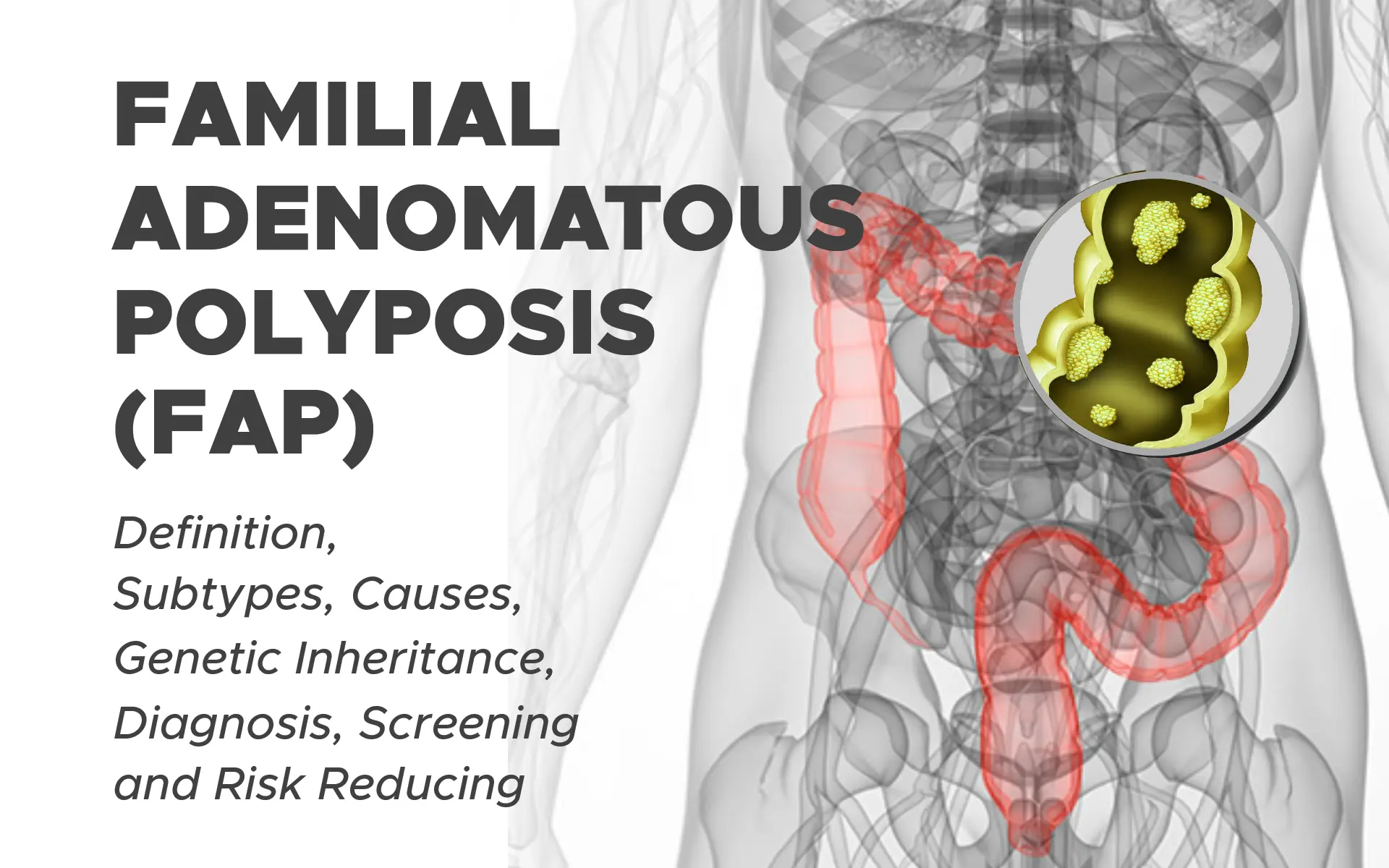
What is Familial Adenomatous Polyposis?
Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) is a genetic condition characterized by the development of numerous polyps in the colon and rectum, increasing the risk of colorectal cancer. Treatment may involve surgery and surveillance.
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Genetic disorder characterized by the development of numerous polyps in the colon and rectum

Symptoms
Multiple polyps in the colon and rectum, increasing the risk of colorectal cancer

Diagnosis
Genetic testing, colonoscopy

Prognosis
Variable, high risk of colorectal cancer

Complications
Colorectal cancer, complications affecting the digestive system
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Inherited mutation in the APC gene; autosomal dominant inheritance

Treatments
Surveillance through colonoscopies, surgery to remove polyps, colectomy in some cases

Prevention
Surveillance through colonoscopies, surgery to remove polyps, colectomy in some cases
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Genetic disorder characterized by the formation of numerous polyps in the colon

Patient Perspectives
Surveillance, polyp removal, sometimes surgery
This information aims to provide a general understanding of the subject matter, but individual circumstances can vary significantly. Please remember to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and guidance.
Share: