Can Disk Herniation be Cured?
Depends on severity
Conservative measures often resolve mild cases; surgery may be needed in severe cases
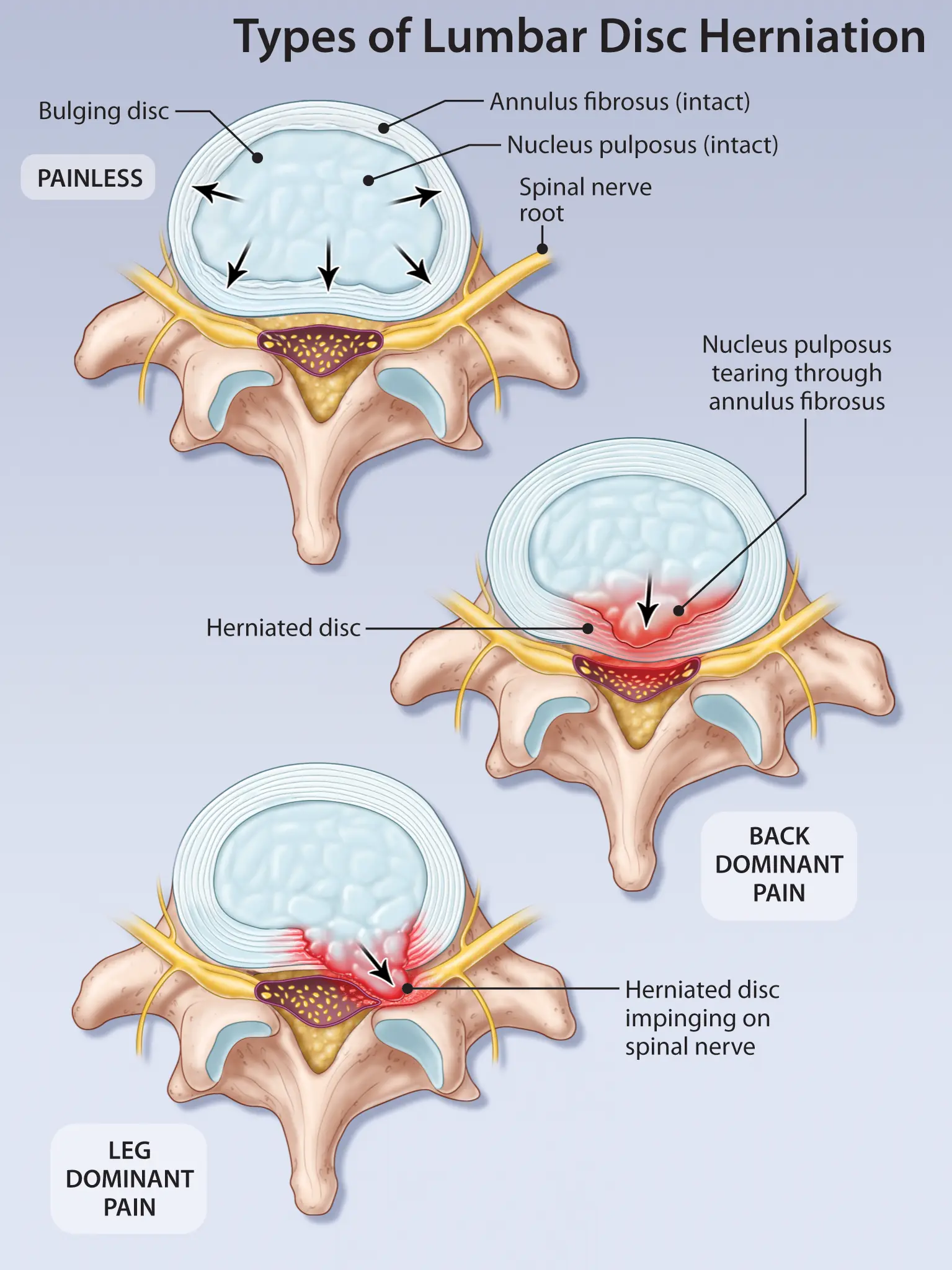
What is Disk Herniation?
Disk herniation, also known as a herniated or slipped disc, occurs when the soft center of a spinal disc pushes through a crack in the tougher exterior. It can cause pain and nerve compression. Treatment may include rest, physical therapy, and, in some cases, surgery.
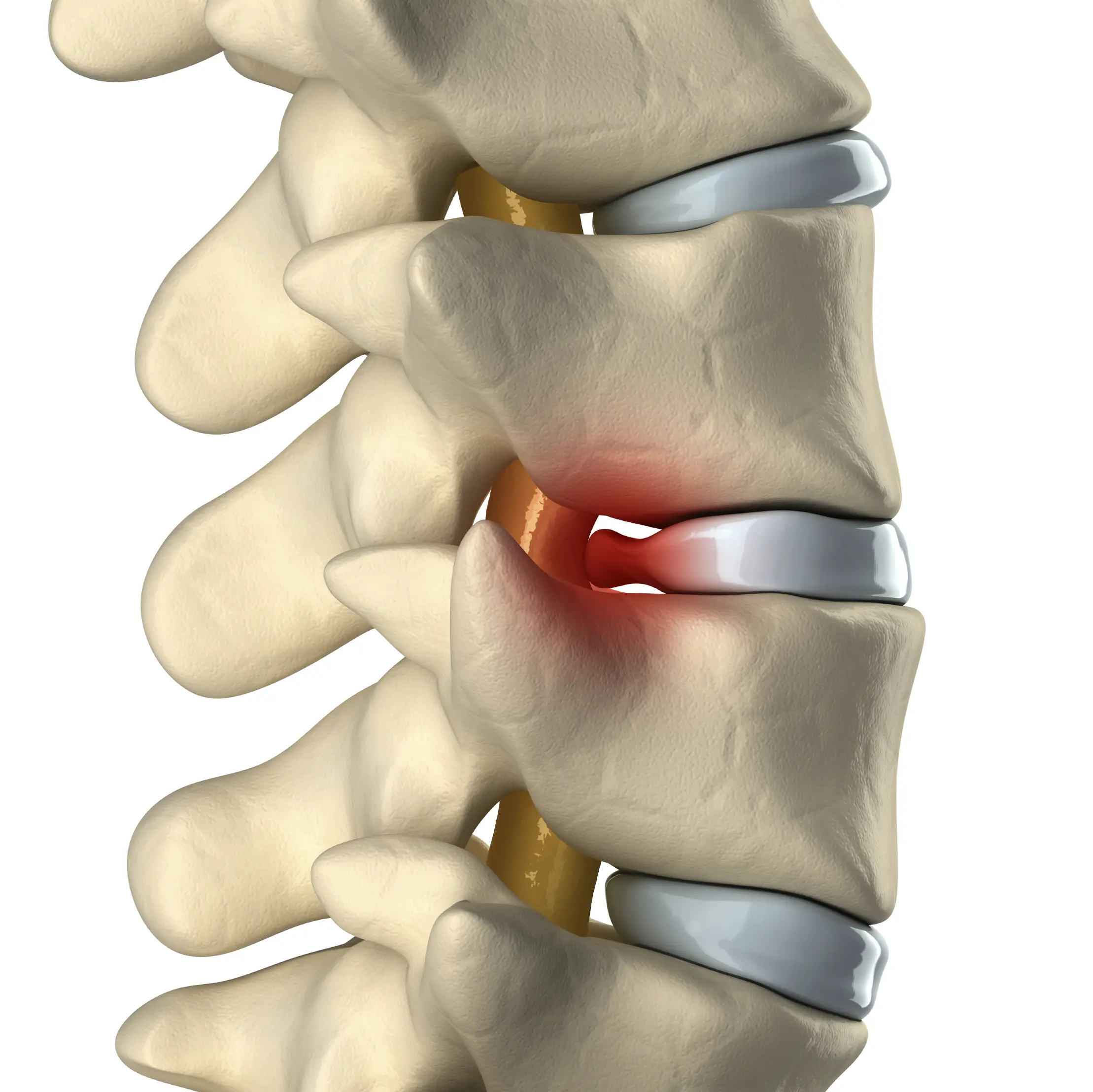
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Bulging or ruptured intervertebral disc

Symptoms
Back or neck pain, numbness, weakness

Diagnosis
Clinical evaluation, imaging studies

Prognosis
Variable, depends on the location and severity of the herniation

Complications
Nerve compression, complications affecting motor and sensory function
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Aging, injury, poor posture

Treatments
Rest, physical therapy, medications, sometimes surgery

Prevention
Rest, physical therapy, medications, sometimes surgery
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Protrusion or rupture of the intervertebral disk, often causing pressure on spinal nerves

Patient Perspectives
Conservative measures, physical therapy, sometimes surgery
Please note that the information provided is based on the current understanding of these conditions and treatments may vary based on individual circumstances. Always consult with a healthcare provider for accurate information.
Share: