Can Coronary Artery Disease be Cured?
Sometimes
While coronary artery disease may not be fully cured, management aims to reduce symptoms, slow progression, and lower the risk of complications
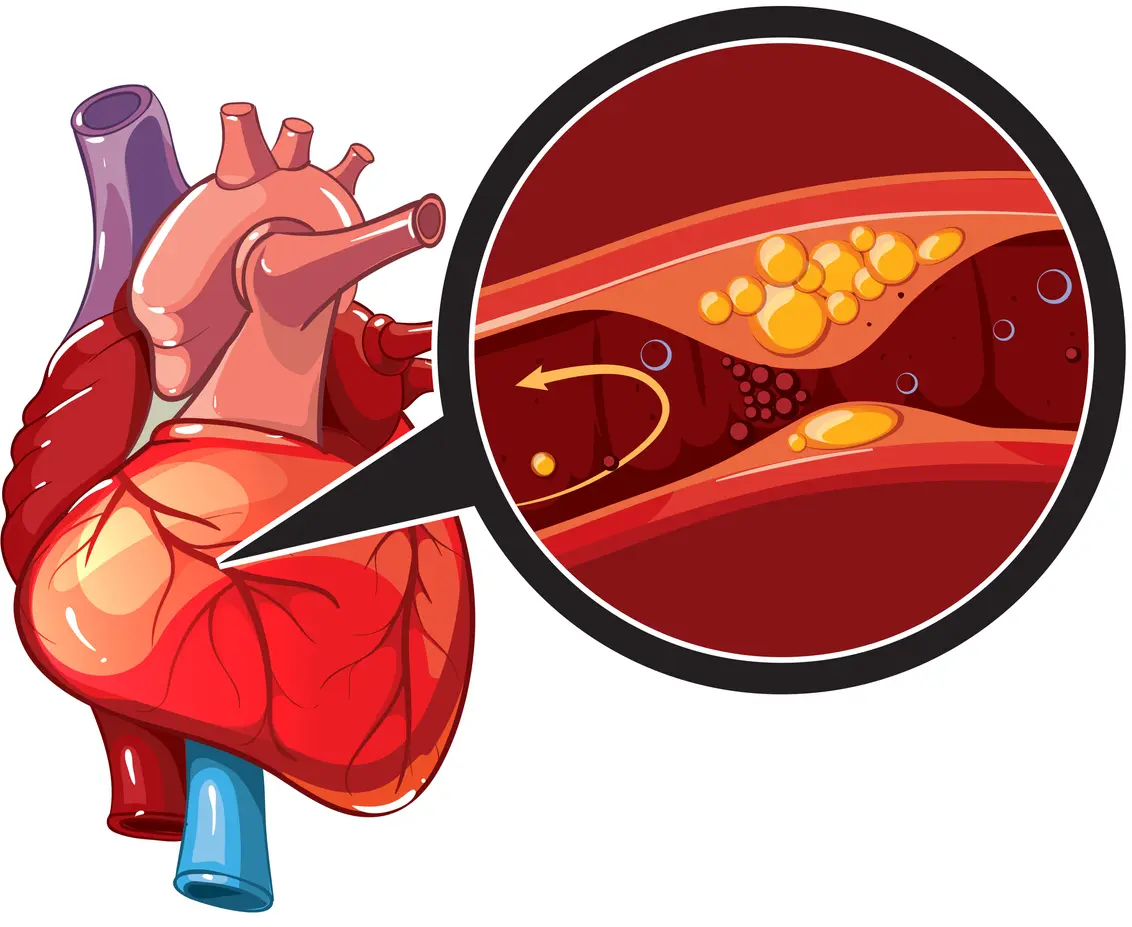
What is Coronary Artery Disease?
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries, leading to reduced blood flow to the heart. Lifestyle changes, medications, and interventions like angioplasty or bypass surgery are common treatments.
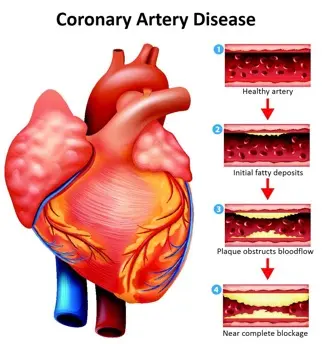
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart muscle

Symptoms
Chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, heart attack

Diagnosis
Clinical evaluation, imaging, blood tests

Prognosis
Variable, depends on intervention and risk factor control

Complications
Myocardial infarction, heart failure
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Atherosclerosis (buildup of plaque in the arteries), risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking

Treatments
Lifestyle changes (diet, exercise), medications (statins, antiplatelets), angioplasty, bypass surgery

Prevention
Lifestyle changes (diet, exercise), medications (statins, antiplatelets), angioplasty, bypass surgery
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Common globally, associated with aging

Patient Perspectives
Long-term lifestyle changes crucial for management
Please remember that this information is provided for general understanding, and individual cases may vary. Always consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and information.
Share: