Can Chronic Nephritis be Cured?
Sometimes
Outcomes depend on the underlying cause and the extent of kidney damage; management focuses on slowing the progression and preventing complications
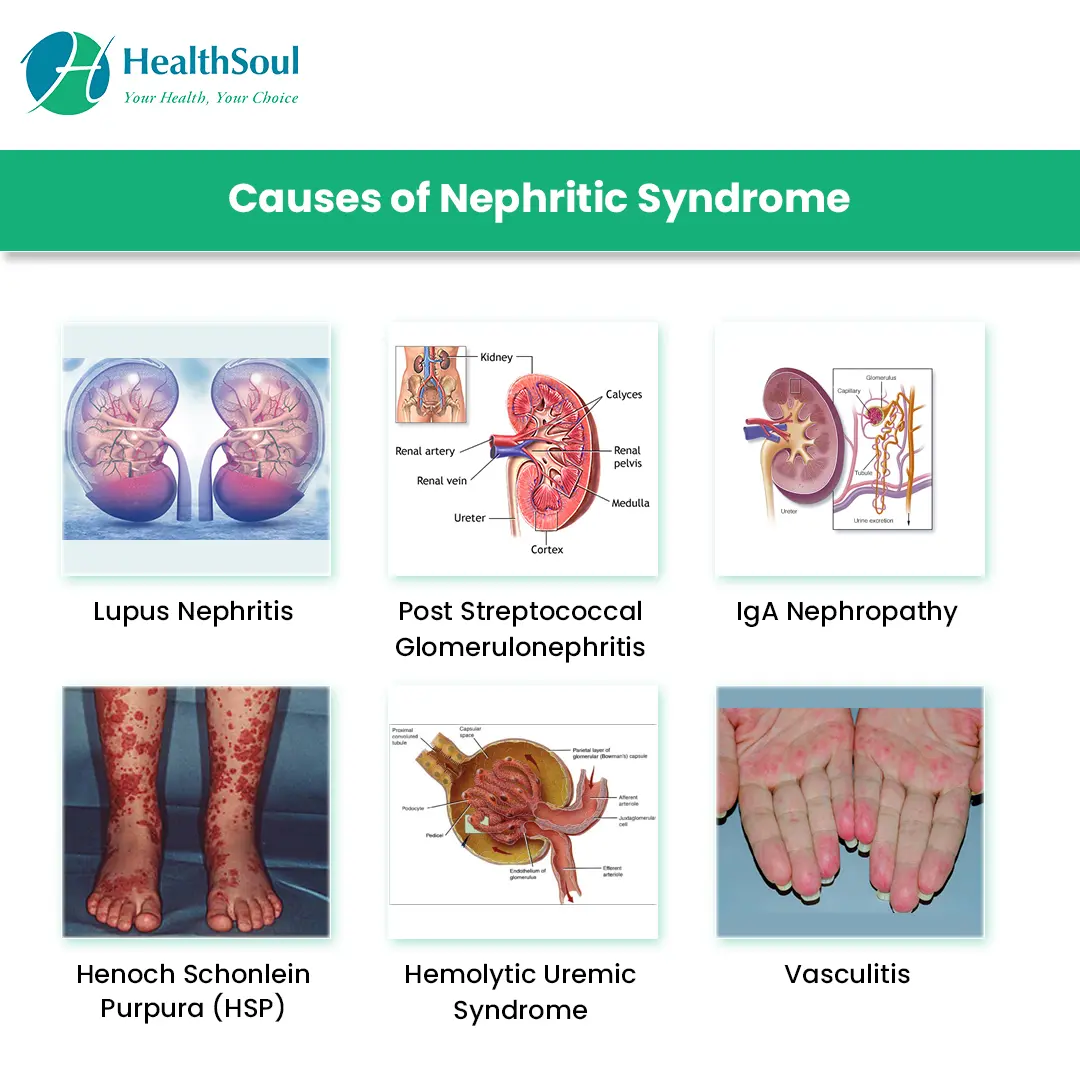
What is Chronic Nephritis?
Chronic nephritis refers to inflammation of the kidneys that persists over time, leading to kidney damage. Causes can include infections, autoimmune conditions, and other factors. Treatment aims to manage the underlying cause and slow the progression of kidney damage.

Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Inflammation of the kidneys that persists for an extended period, often leading to kidney damage and impaired function

Symptoms
Blood in urine, proteinuria, hypertension, swelling in the legs and face

Diagnosis
Blood tests, imaging studies, sometimes kidney biopsy

Prognosis
Variable, depends on the underlying cause and management

Complications
Kidney failure, complications affecting multiple organs
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Various underlying causes, including autoimmune disorders, infections, and other kidney diseases

Treatments
Management of underlying cause, medications to control symptoms and complications

Prevention
Management of underlying cause, medications to control symptoms and complications
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Inflammation of the kidneys, often associated with chronic kidney disease

Patient Perspectives
Management of underlying causes, supportive care
Remember, the information provided here is intended for general knowledge purposes and may not apply to every individual case. To ensure you have accurate information relevant to your specific situation, always consult with a healthcare professional.
Share: