Can Asymptomatic Bacteriuria be Cured?
No
Often does not require treatment; antibiotic therapy may be considered in certain situations
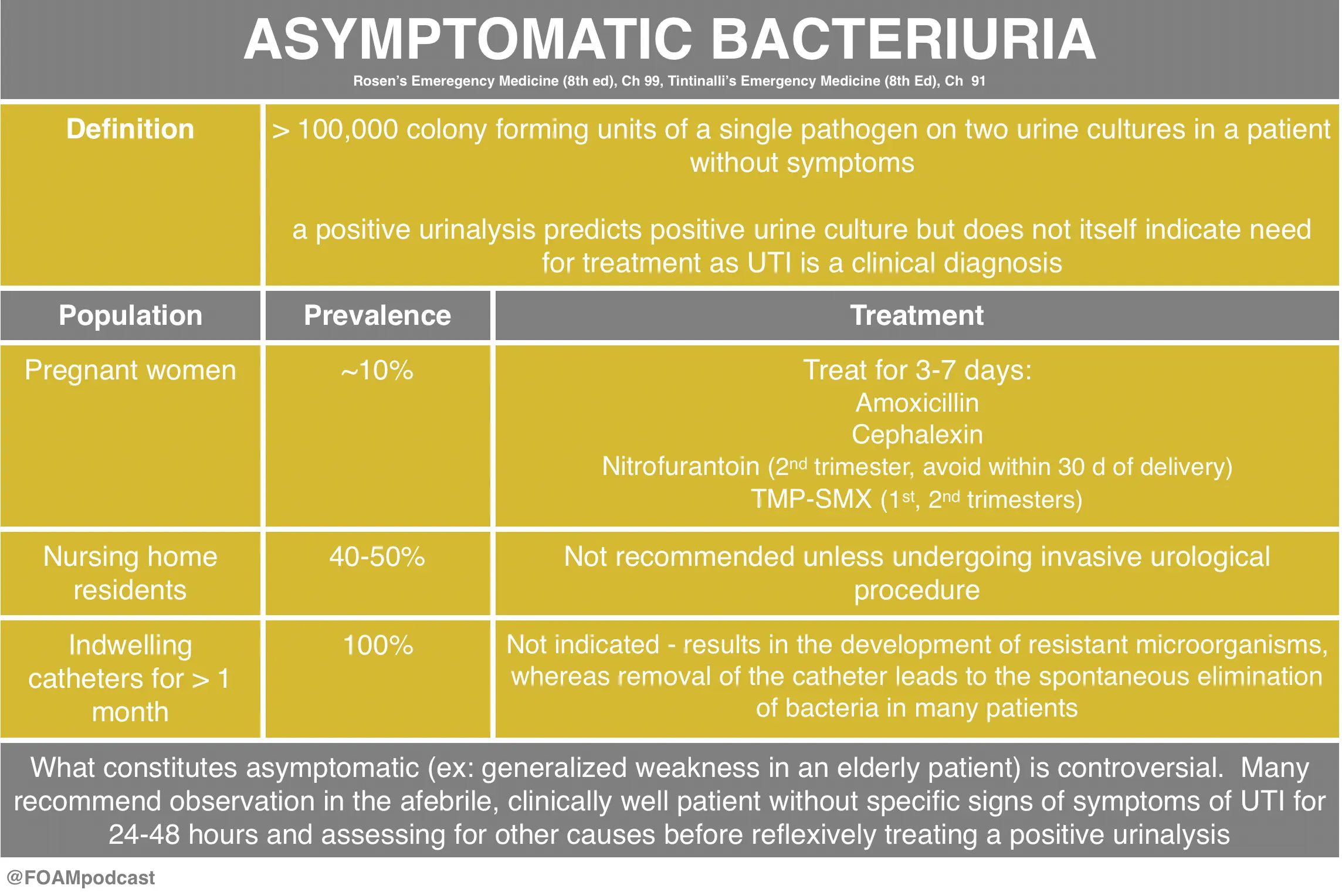
What is Asymptomatic Bacteriuria?
Asymptomatic bacteriuria is the presence of bacteria in the urine without symptoms of a urinary tract infection. It is common in certain populations and may not require treatment unless specific risk factors are present.

Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Presence of bacteria in the urine without causing symptoms or urinary tract infection

Symptoms
Typically no symptoms; may be detected during routine urine testing

Diagnosis
Urinalysis, urine culture

Prognosis
Generally good; may not require treatment

Complications
Increased risk of urinary tract infections
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Various factors, including sexual activity, urinary tract abnormalities, or catheter use

Treatments
Generally not treated unless there are specific risk factors or pregnancy

Prevention
Generally not treated unless there are specific risk factors or pregnancy
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Common finding, especially in older adults

Patient Perspectives
Individualized approach based on the patient’s overall health and circumstances
While the information presented here reflects the current knowledge about these conditions and treatments, it’s important to understand that individual cases may differ. Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial for accurate information tailored to your specific needs.
Share: