Can Arterial Embolism be Cured?
Yes
Timely treatment can restore blood flow and prevent tissue damage
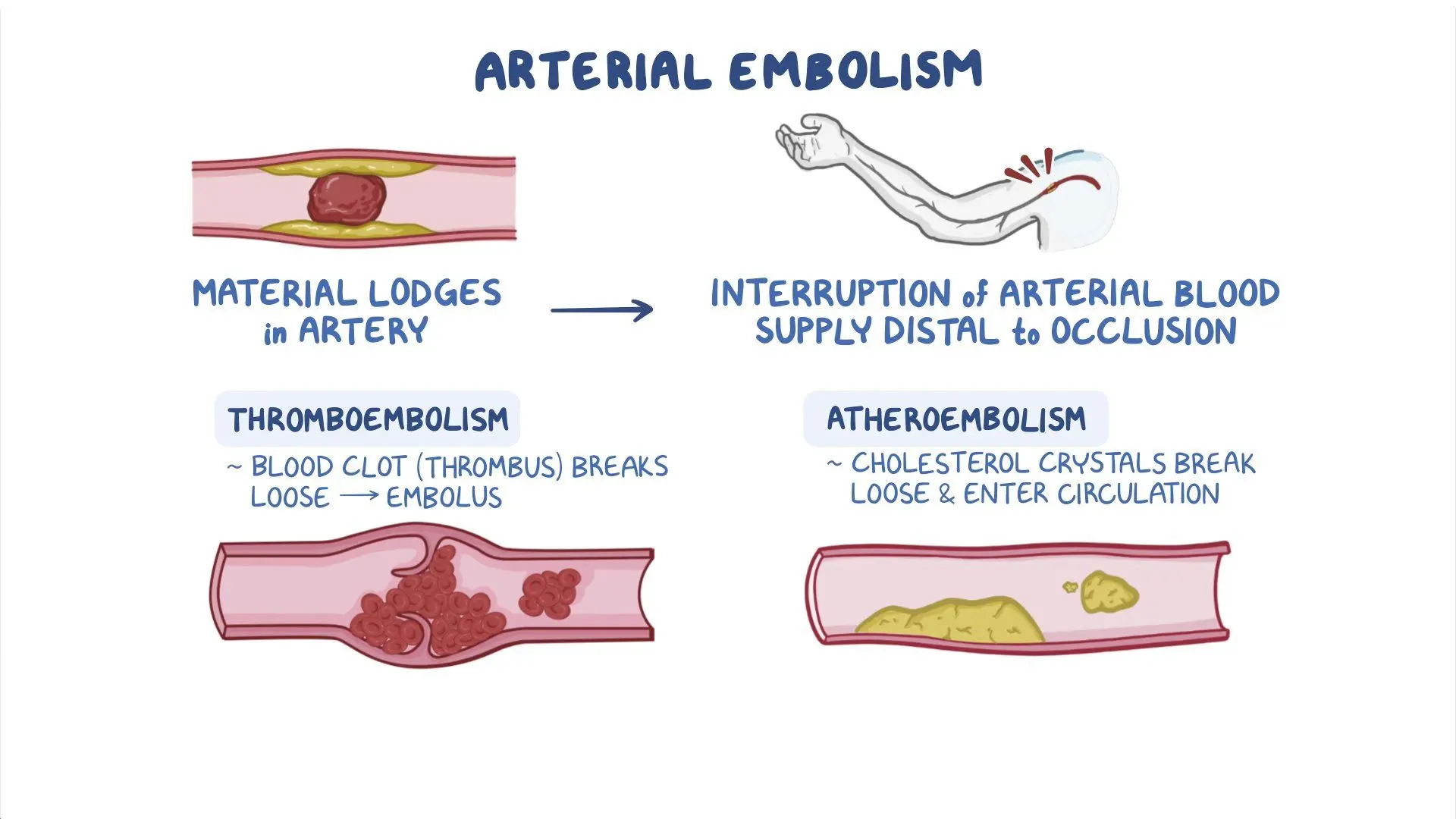
What is Arterial Embolism?
Arterial embolism occurs when a blood clot or other material travels through the bloodstream and blocks an artery. This can lead to decreased blood flow and tissue damage. Treatment involves addressing the cause, such as anticoagulant medications or surgical removal of the embolism.
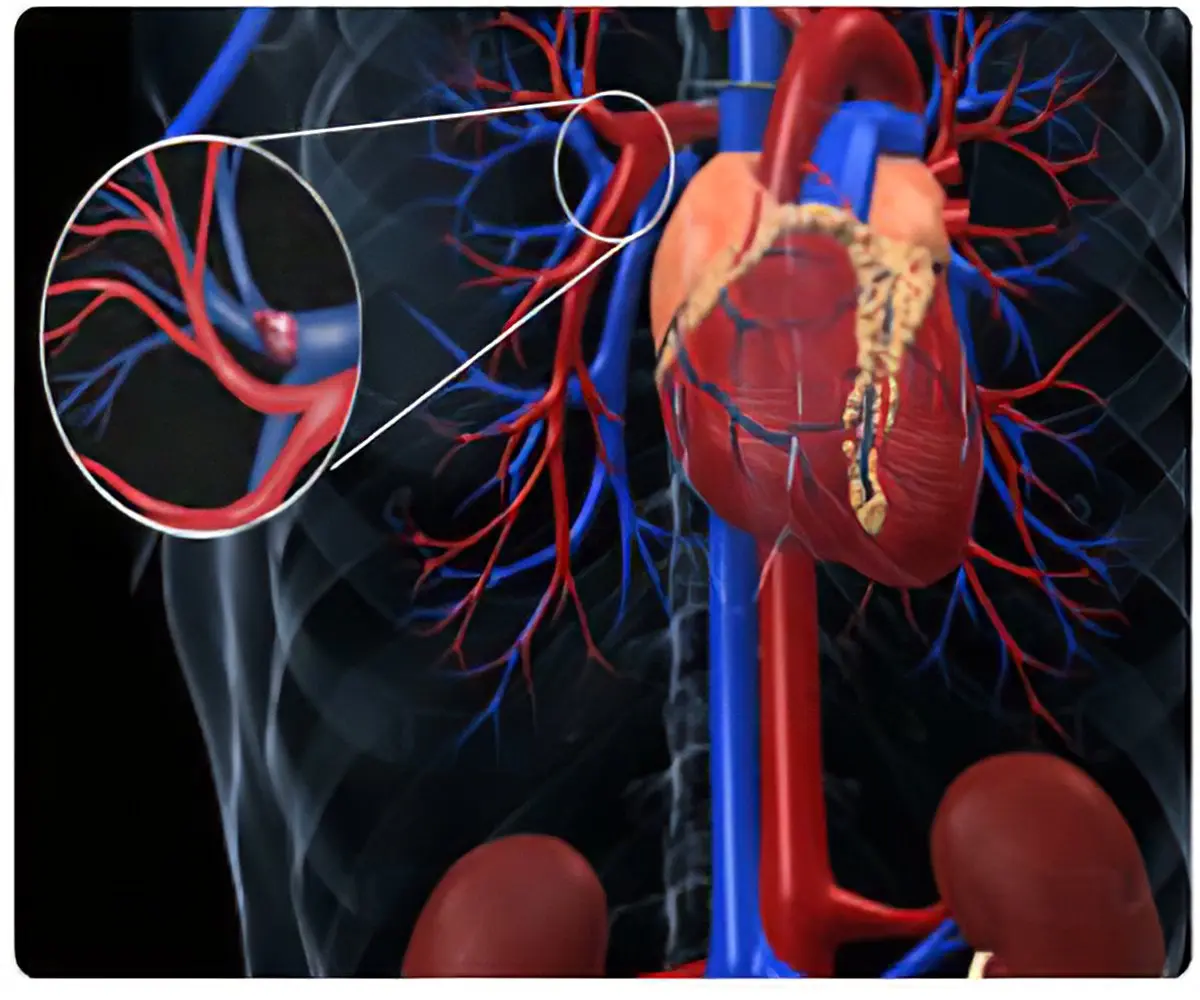
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Blockage of an artery by an embolus (clot or debris)

Symptoms
Sudden onset of symptoms in affected area

Diagnosis
Imaging studies, blood tests

Prognosis
Variable; depends on the specific type and location

Complications
Organ damage, stroke, limb ischemia
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Blood clots, debris, fat particles

Treatments
Anticoagulation, thrombolytic therapy, surgery

Prevention
Anticoagulation, thrombolytic therapy, surgery
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Can result from various conditions, including atrial fibrillation

Patient Perspectives
Prevention and early treatment of underlying conditions are crucial
This information aims to provide a general understanding of the subject matter, but individual circumstances can vary significantly. Please remember to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and guidance.
Share: