Can American Trypanosomiasis be Cured?
No
Treatment can control the infection, but complete cure is rare
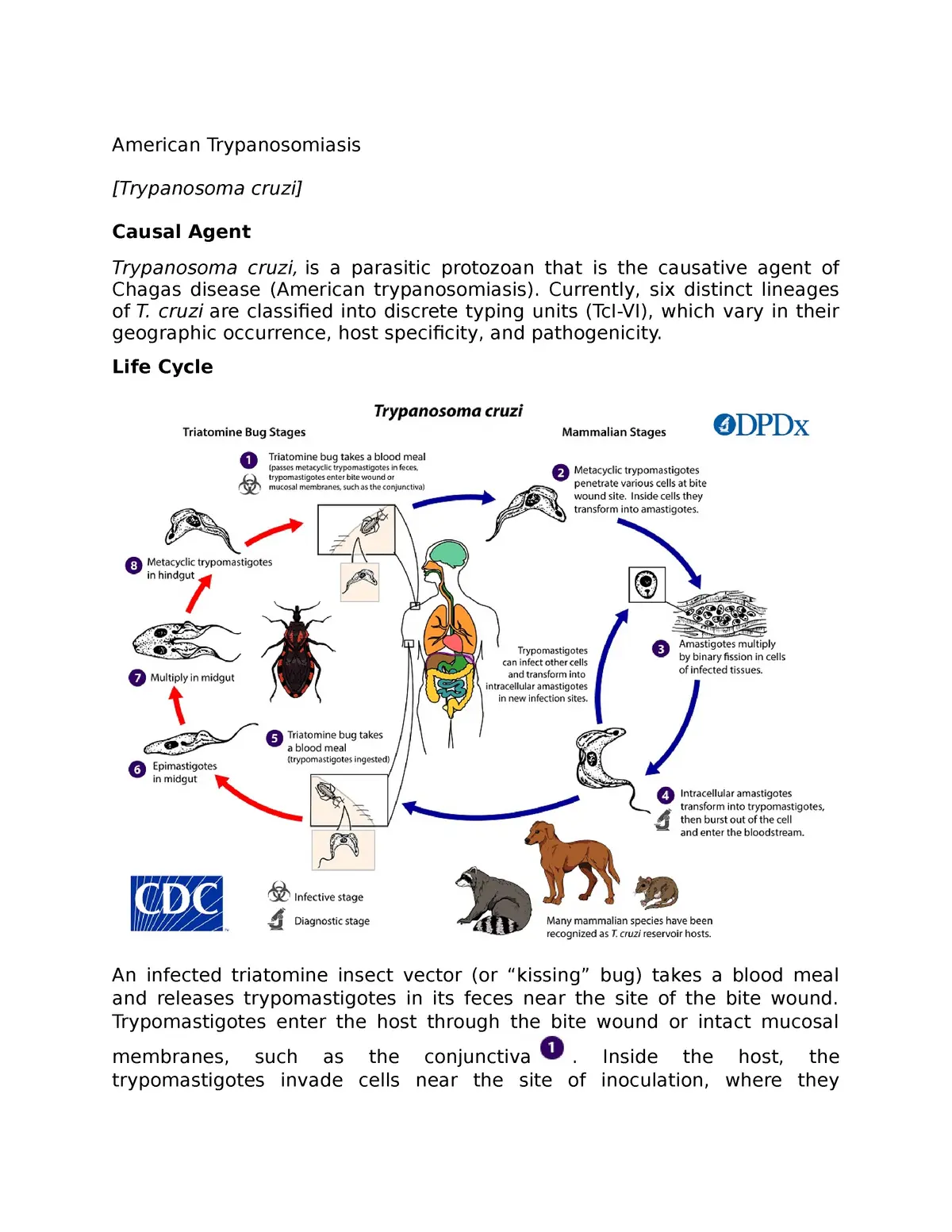
What is American Trypanosomiasis?
American trypanosomiasis, also known as Chagas disease, is a tropical parasitic infection caused by the protozoan parasite Trypanosoma cruzi. It is primarily transmitted to humans by triatomine bugs. The disease has acute and chronic phases, with symptoms ranging from mild to severe, including fever, fatigue, and heart or digestive system issues. Treatment is more effective in the acute phase, and antiparasitic medications are commonly used.
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Parasitic infection caused by Trypanosoma cruzi

Symptoms
Fever, fatigue, swollen glands, heart issues

Diagnosis
Blood tests, xenodiagnosis, polymerase chain reaction

Prognosis
Variable; acute and chronic stages with potential complications

Complications
Chronic heart and digestive problems
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Triatomine bug bites, blood transfusion, congenital

Treatments
Antiparasitic medications (benznidazole, nifurtimox)

Prevention
Antiparasitic medications (benznidazole, nifurtimox)
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Common in certain regions of the Americas; transmitted by kissing bugs

Patient Perspectives
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for preventing complications
Please note that the information provided is based on the current understanding of these conditions and treatments may vary based on individual circumstances. Always consult with a healthcare provider for accurate information.
Share: