Can Acute Glomerulonephritis be Cured?
Maybe
Can be reversible with prompt and appropriate treatment; outcomes depend on the cause and extent of kidney damage
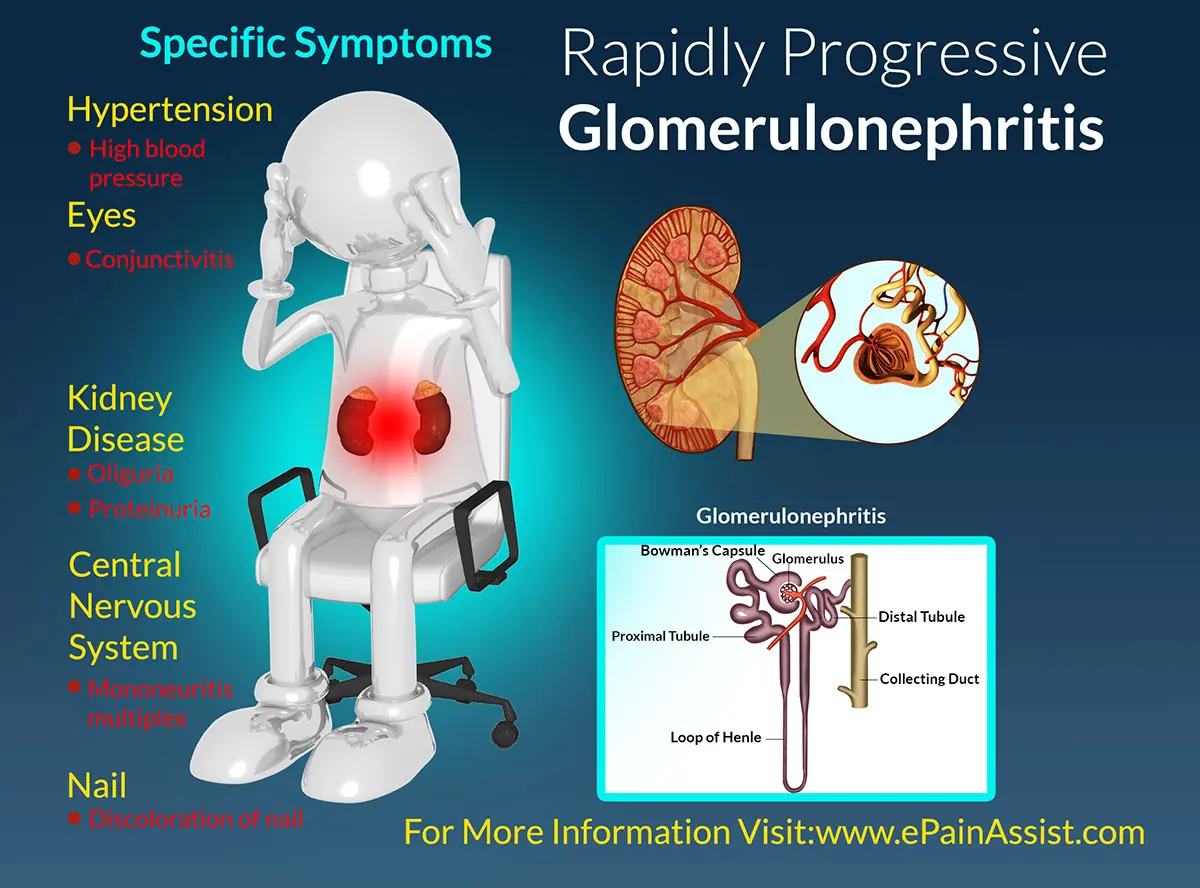
What is Acute Glomerulonephritis?
Acute glomerulonephritis is inflammation of the kidney’s glomeruli. Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may involve medications. Regular monitoring is important for assessing kidney function and managing symptoms.

Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Inflammation of the glomeruli in the kidneys, often a result of an immune response

Symptoms
Hematuria (blood in urine), proteinuria, edema; may follow infections

Diagnosis
Urinalysis, blood tests, kidney biopsy

Prognosis
Variable; some cases resolve, others progress to chronic kidney disease

Complications
Hypertension, kidney failure
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Infections (particularly streptococcal), autoimmune conditions

Treatments
Antibiotics (if bacterial cause), corticosteroids, supportive care; management depends on underlying cause

Prevention
Antibiotics (if bacterial cause), corticosteroids, supportive care; management depends on underlying cause
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Can occur at any age; often follows streptococcal infections

Patient Perspectives
Monitoring and managing underlying conditions are important
This information aims to provide a general understanding of the subject matter, but individual circumstances can vary significantly. Please remember to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and guidance.
Share: