Can Steatohepatitis be Cured?
Sometimes
Management can improve outcomes, but complete resolution may not always be achievable; outcomes depend on the extent of liver damage and response to intervention
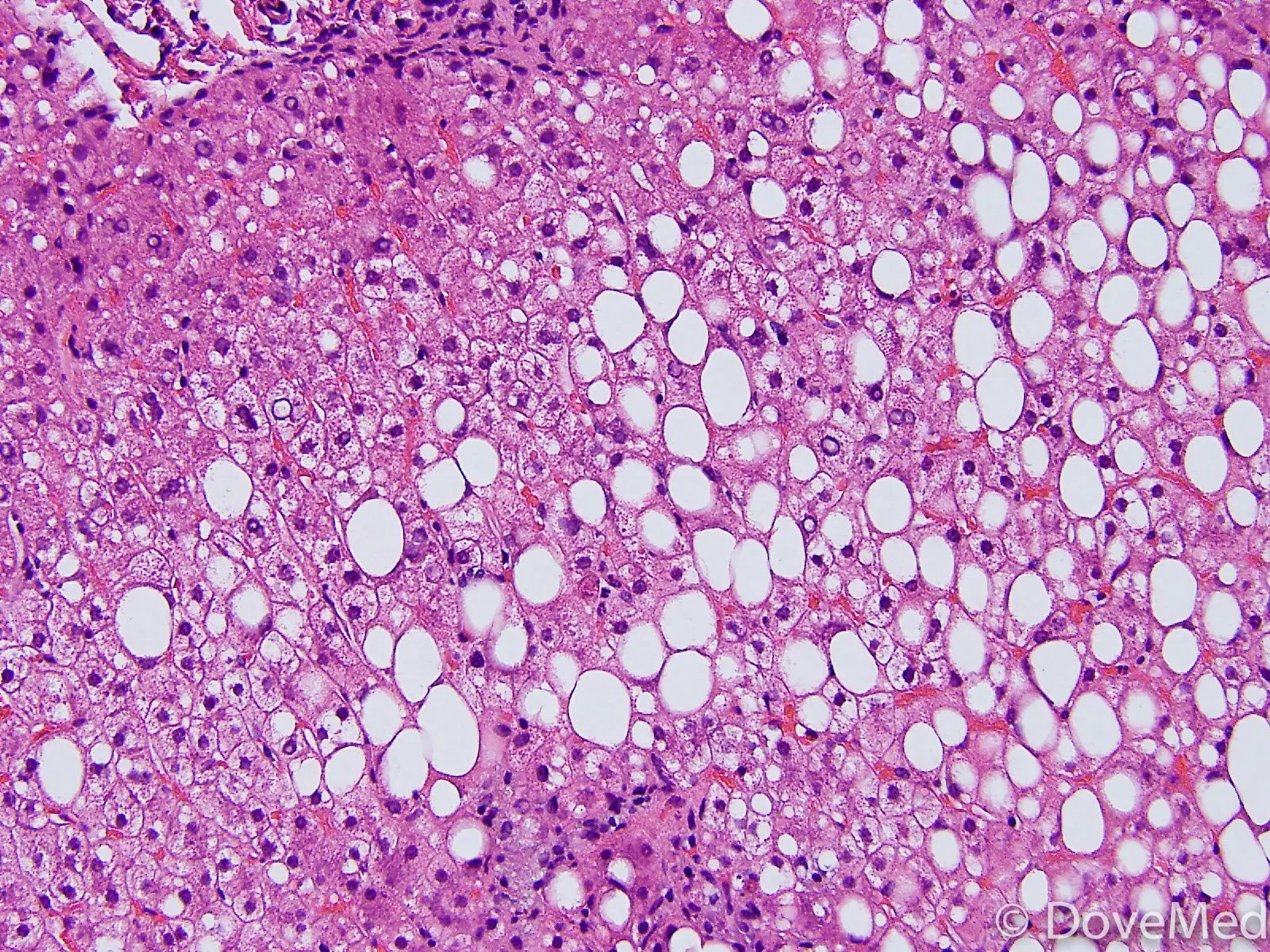
What is Steatohepatitis?
Steatohepatitis is inflammation of the liver associated with fat accumulation. It is often seen in the context of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Treatment involves lifestyle modifications and, in some cases, medications. Regular monitoring is important for assessing liver function, managing risk factors, and preventing complications.
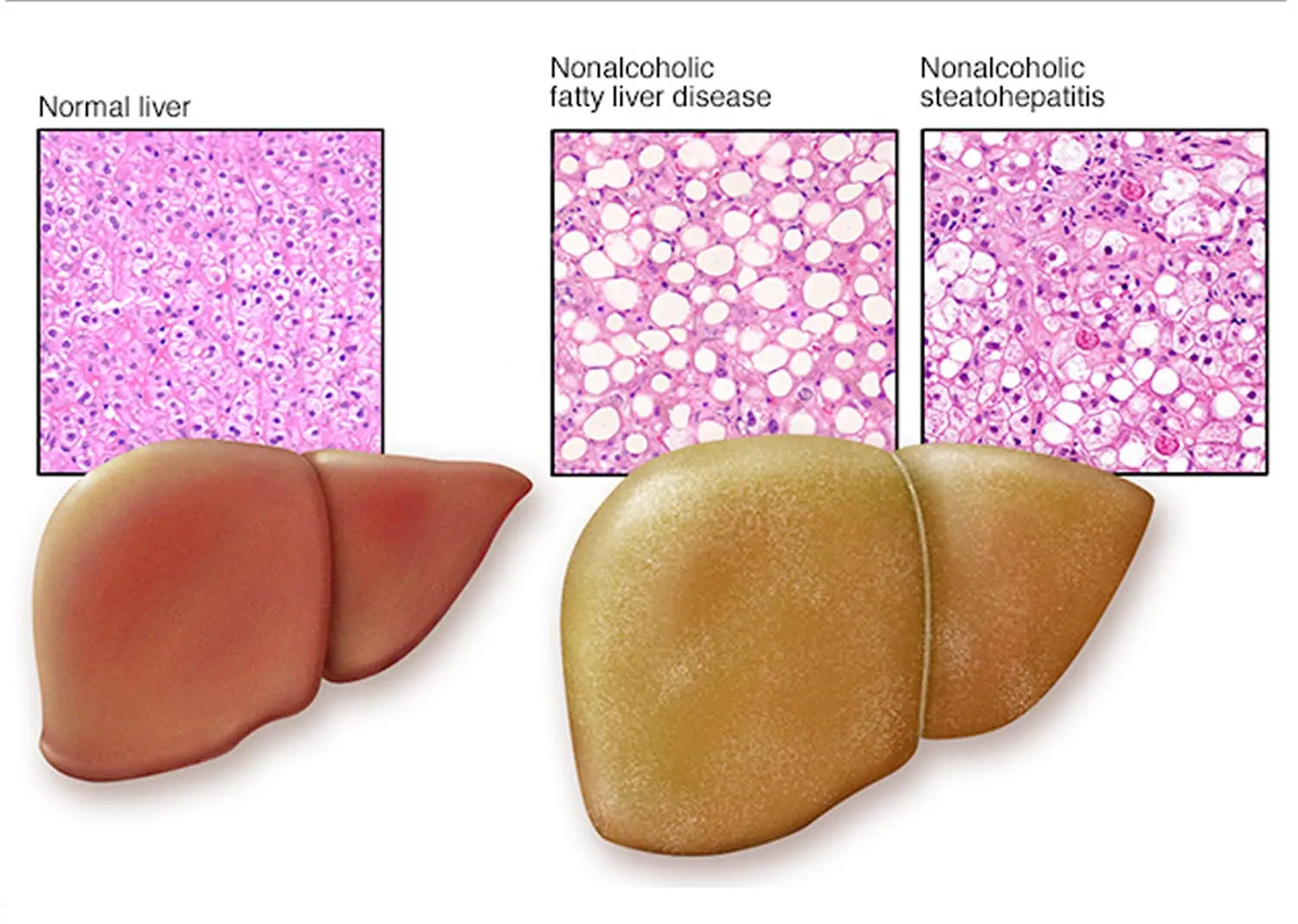
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Inflammation of the liver with fat accumulation, often associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)

Symptoms
Fatigue, enlarged liver, abdominal discomfort

Diagnosis
Clinical evaluation, imaging studies

Prognosis
Variable, depends on the progression of the disease

Complications
Liver fibrosis, complications affecting liver function
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Obesity, insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome

Treatments
Lifestyle changes (diet, exercise), weight loss, management of underlying conditions

Prevention
Lifestyle changes (diet, exercise), weight loss, management of underlying conditions
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Inflammation of the liver due to fat accumulation

Patient Perspectives
Lifestyle modifications, weight loss, sometimes medications
Please note that the information provided is based on the current understanding of these conditions and treatments may vary based on individual circumstances. Always consult with a healthcare provider for accurate information.
Share: