Can Stable Angina be Cured?
Sometimes
Stable angina can often be managed effectively with treatment, but it is a chronic condition; outcomes depend on the extent of coronary artery disease and response to therapy
What is Stable Angina?
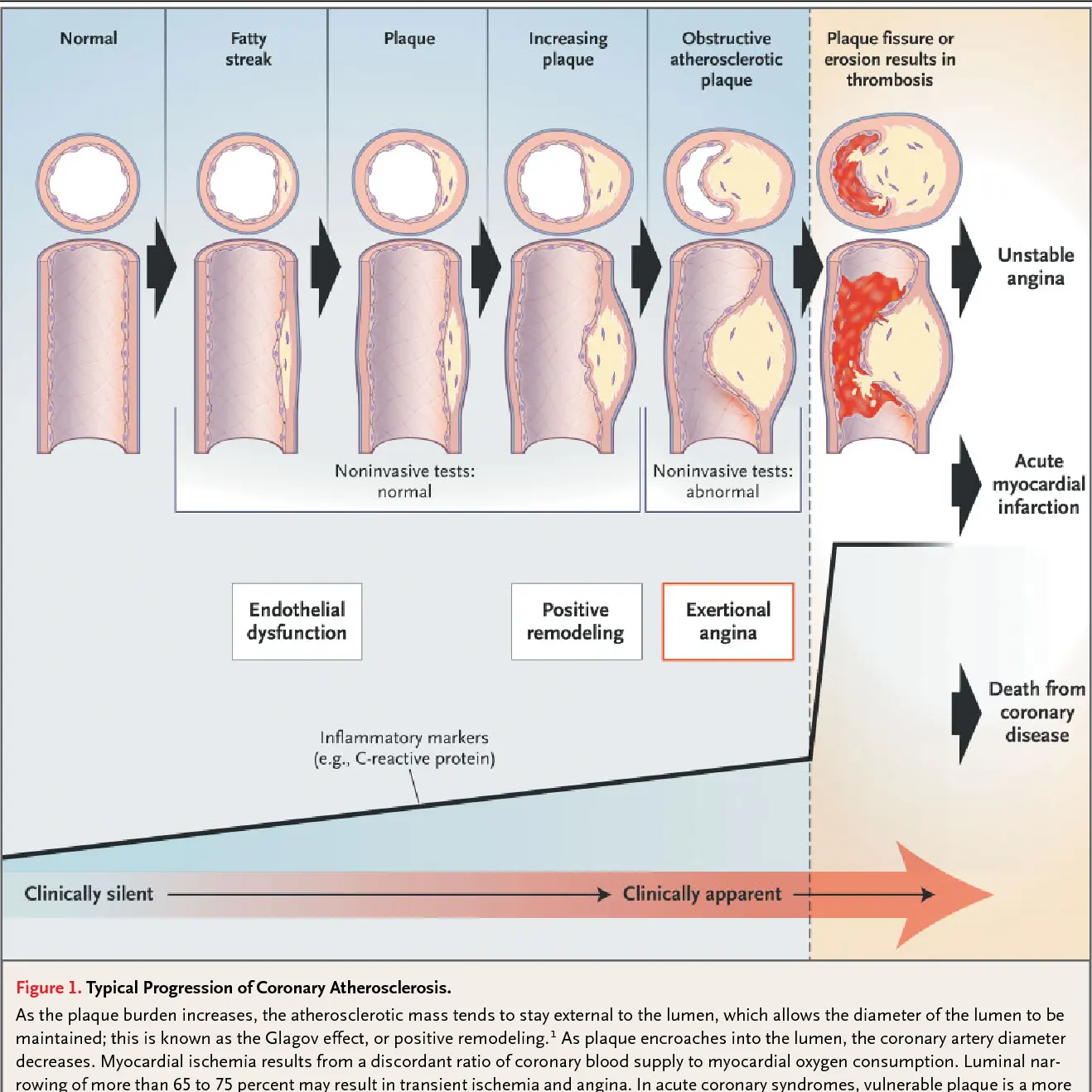
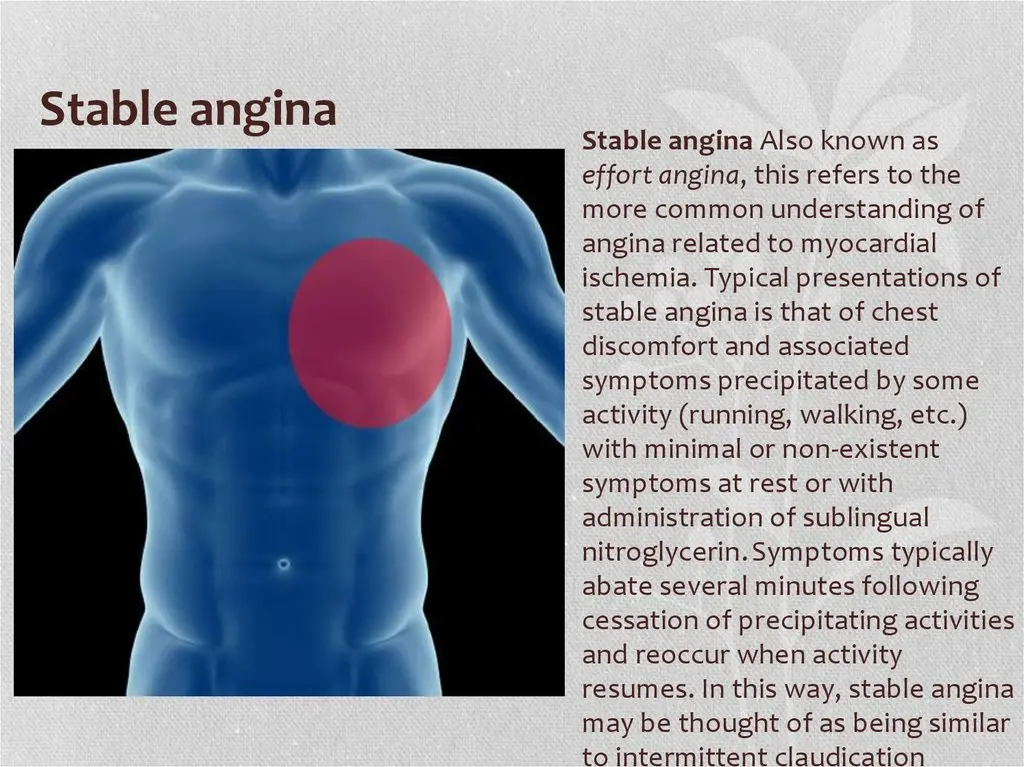
Stable angina is chest pain or discomfort that occurs with exertion or stress. Treatment includes medications, lifestyle modifications, and sometimes procedures like angioplasty. Regular monitoring is important for assessing symptoms, adjusting treatment, and preventing complications.
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Chest pain or discomfort due to reduced blood flow to the heart muscle

Symptoms
Chest pain or discomfort, often triggered by exertion or stress

Diagnosis
Clinical evaluation, imaging studies

Prognosis
Generally manageable with appropriate care

Complications
Heart attack, complications affecting cardiovascular health
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Coronary artery disease, atherosclerosis, reduced blood flow to the heart

Treatments
Lifestyle changes, medications (nitroglycerin, beta-blockers), angioplasty, coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG)

Prevention
Lifestyle changes, medications (nitroglycerin, beta-blockers), angioplasty, coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG)
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Chest pain or discomfort due to reduced blood flow to the heart

Patient Perspectives
Medications, lifestyle modifications, sometimes invasive procedures
While the information presented here reflects the current knowledge about these conditions and treatments, it’s important to understand that individual cases may differ. Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial for accurate information tailored to your specific needs.
Share: