Can Primary Immunodeficiency be Cured?
No
Primary immunodeficiencies are typically lifelong conditions; management aims to strengthen the immune system and prevent infections
What is Primary Immunodeficiency?
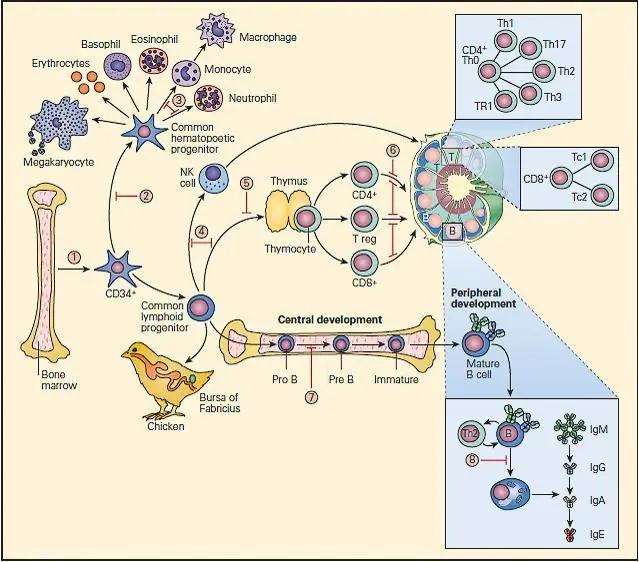
Primary immunodeficiency refers to a group of genetic disorders where the immune system is weakened. Treatment involves immunoglobulin replacement therapy and, in some cases, stem cell transplant.

Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Group of disorders characterized by a weakened immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections

Symptoms
Frequent infections, slow wound healing, autoimmune disorders

Diagnosis
Immunological tests, genetic testing

Prognosis
Variable; depends on the specific type and severity of the disorder

Complications
Recurrent infections, complications of untreated primary immunodeficiency
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Genetic mutations affecting immune system function

Treatments
Immunoglobulin replacement therapy, antibiotics, bone marrow transplantation

Prevention
Immunoglobulin replacement therapy, antibiotics, bone marrow transplantation
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Genetic disorders leading to a weakened immune system

Patient Perspectives
Management focuses on preventing infections and supporting immune function
While the information presented here reflects the current knowledge about these conditions and treatments, it’s important to understand that individual cases may differ. Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial for accurate information tailored to your specific needs.
Share: