Can Myelodysplastic Syndromes be Cured?
Depends on type
Management depends on the specific type and severity of the syndrome
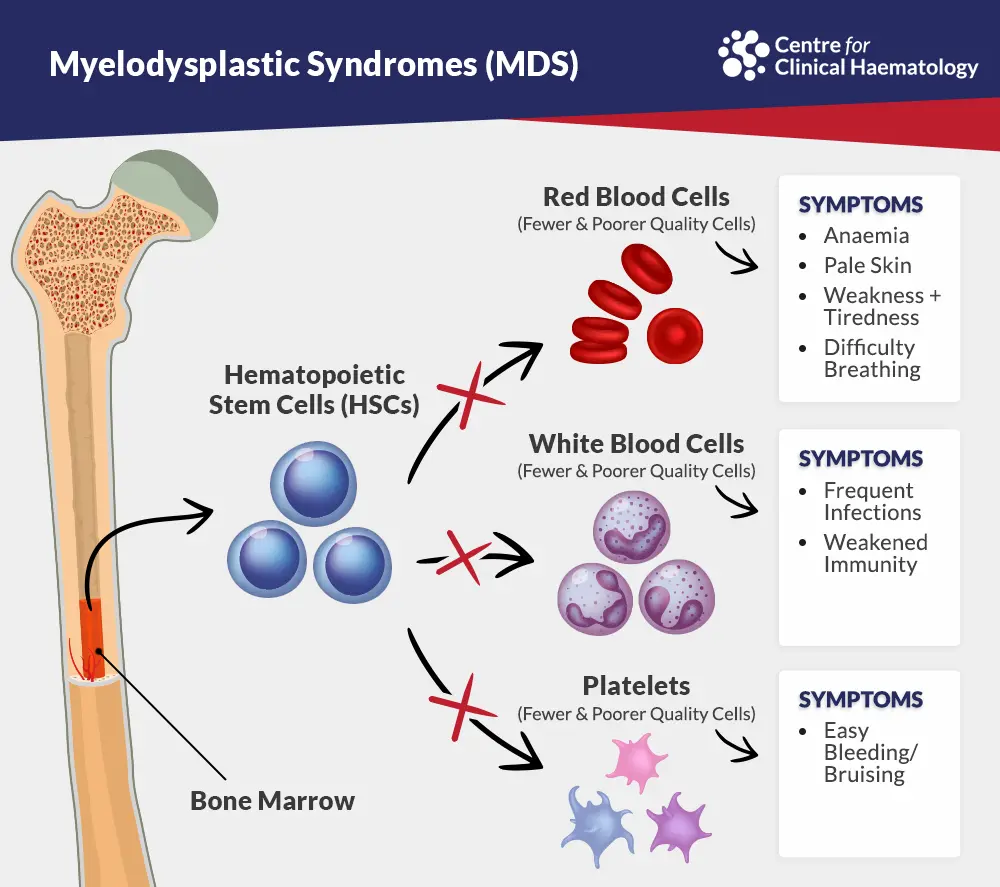
What is Myelodysplastic Syndromes?
Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are a group of blood disorders characterized by ineffective blood cell production. Treatment may involve supportive care, medications, and, in some cases, stem cell transplantation. Regular monitoring is important to assess disease progression and determine the most appropriate interventions. A multidisciplinary approach may be used to address various aspects of MDS.
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Disorders characterized by ineffective blood cell production

Symptoms
Fatigue, anemia, increased risk of infections

Diagnosis
Blood tests, bone marrow biopsy

Prognosis
Variable; depends on the specific type and progression of the disease

Complications
AML transformation, complications of untreated myelodysplastic syndromes
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Genetic mutations, exposure to certain chemicals

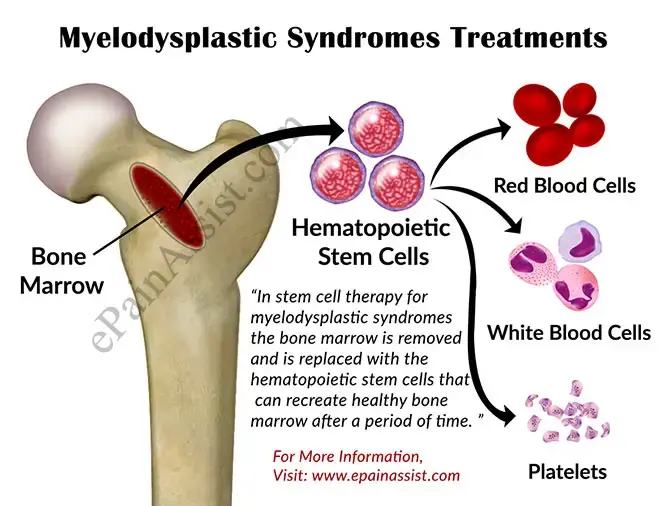
Treatments
Supportive care, blood transfusions, stem cell transplant

Prevention
Supportive care, blood transfusions, stem cell transplant
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Disorders affecting the production of blood cells

Patient Perspectives
Prognosis varies based on the type and response to treatment
This information aims to provide a general understanding of the subject matter, but individual circumstances can vary significantly. Please remember to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and guidance.
Share: