Can Mononucleosis be Cured?
Sometimes
Mononucleosis is usually self-limiting, and symptoms resolve with time; there is no specific cure, but management focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing complications
What is Mononucleosis?
Mononucleosis, or “mono,” is an infectious illness caused by the Epstein-Barr virus. Symptoms may include fever, sore throat, and swollen lymph nodes. Treatment is supportive, focusing on rest, hydration, and pain management. Complications are rare but can occur, and careful monitoring is important, especially for complications involving the liver or spleen.
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Viral infection caused by the Epstein-Barr virus, often known as “mono” or the “kissing disease”

Symptoms
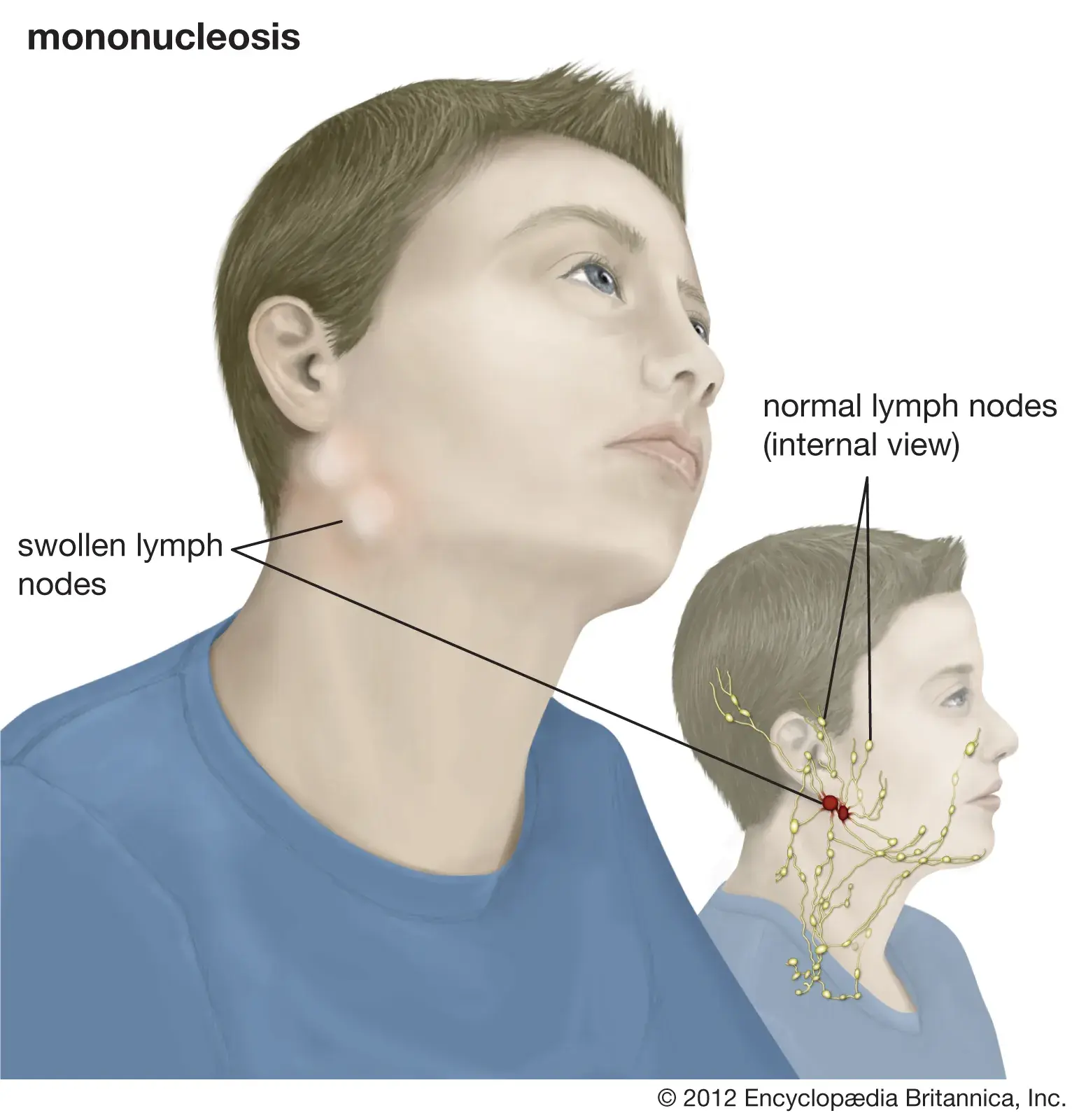
Fatigue, sore throat, fever, swollen lymph nodes, rash

Diagnosis
Blood tests, sometimes throat culture

Prognosis
Generally good with appropriate management and treatment

Complications
Enlarged spleen, complications of severe cases
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Epstein-Barr virus, close contact with infected individuals

Treatments
Supportive care, rest, pain relievers, corticosteroids in severe cases

Prevention
Supportive care, rest, pain relievers, corticosteroids in severe cases
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Viral infection caused by the Epstein-Barr virus

Patient Perspectives
Rest and supportive care are key for recovery
Please note that the information provided is based on the current understanding of these conditions and treatments may vary based on individual circumstances. Always consult with a healthcare provider for accurate information.
Share: